ETL Testing Guide
The following chapters provide a comprehensive overview of ETL testing! Here, you will learn about the
basics, various types, proven methods for conducting ETL tests, and the benefits of automated testing. To
successfully perform ETL tests, you should know the areas of databases, data modeling, and SQL. However, a
basic understanding of programming languages is also helpful.
What is ETL testing?
ETL testing is integral to business intelligence (BI) and data warehouse systems. ETL stands for Extract,
Transform, and Load, referring to the three steps performed during data integration. These steps include
extracting data from various sources, transforming it into a standard format, and loading it into the target
system. ETL testing ensures that all data is processed completely and correctly, and that the target system
delivers the right results. This includes tests for data quality, data integrity, and performance.
To perform successful ETL testing, it requires knowledge of data sources and the ETL process, as well as a
comprehensive testing strategy that covers all aspects. SQL queries and automated testing tools are often
used to quickly and effectively identify errors.
Why is ETL testing important?
A faulty ETL process can severely damage a company, leading to inaccurate or missing data. Incorrect
aggregation and misleading reports can influence critical business decisions, cause financial losses, and
have legal consequences. But the most significant risk is the loss of trust from customers and partners who
base their decisions on this erroneous data.
A faulty ETL process can also lead to a loss of time and incomplete or delayed reports and analyses. That's
why ETL testing is integral to BI and data warehouse systems. A careful testing strategy and monitoring of
the ETL process lead to higher data quality and better business decisions, resulting in a more successful
company.
A few definitions of terms
Error: Have you ever wondered what happens when a system or product doesn't work as it
should? That's an error! This can happen due to unclear requirements, incorrect implementation, or
unforeseen problems.
Fault state vs. Fault effect: In a fault state, a system or product is
affected by an error that impairs its functionality. But what happens exactly? The fault effect describes
the consequences of an error on the system or product and its environment. The impact can vary depending on
the location and type of error. Some errors can cause only minor restrictions, while others are so severe
that the system or product becomes unusable.
Error masking: Sometimes, an error hides behind other errors or disturbances that obscure
the real problem. This can lead us to draw false conclusions and be misled. This phenomenon is called error
masking and is a real challenge for anyone trying to solve problems.
Testing: Testing is like detective work; you want to detect and eliminate errors to ensure a
system or product works perfectly. The testing process uses various tools and techniques to help identify
possible causes of errors. Ultimately, it's about maximizing quality and minimizing potential negative
impacts.
These terms are intertwined and influence each other. A single error can lead to a chain reaction, which can
have unforeseeable consequences. Identifying and correcting errors can be challenging if they are masked by
something else. Testing is crucial to finding and eliminating errors and ensuring that everything works as
intended.
Testing costs vs. failure costs
Testing costs and failure costs are two essential terms in quality assurance. While testing costs include the
costs of conducting tests and test infrastructure, failure costs refer to the potentially expensive
consequences of errors that were not detected and fixed. These can range from production downtime to
reputation-damaging image losses. It is, therefore, advisable to invest in quality assurance measures to
avoid potential failure costs and save costs in the long run.
Start quality assurance measures early in development to avoid errors that may spread to other parts of the
system and become more expensive. Detecting and fixing errors early is the most effective way to keep costs
low and improve the final product. Remember that fixing errors later in the process is generally more
costly.
The „Rule of Ten“ in software bug-fixing asserts that the cost of fixing a bug escalates
approximately ten times with each progressive stage in the software lifecycle, from requirements gathering,
design, coding, testing to deployment and maintenance. Therefore, a bug rectified at minimal cost during the
requirement or design phase could potentially cost hundreds or thousands of times more to fix in the
maintenance or post-deployment stages.
How does the ETL testing process work briefly?
In the ETL testing process, test cases are derived from the requirements of the ETL process. Then, a test
plan is created that determines which tests are needed for which strategy. Next, the necessary data is
provided in a particular test environment, and the ETL processes are executed. After that, the target data
is tested, and errors are analyzed if necessary. This process can be repeated, especially for bug fixes or
regression testing. As this is an elaborate process and ETL tests typically work with a large amount of
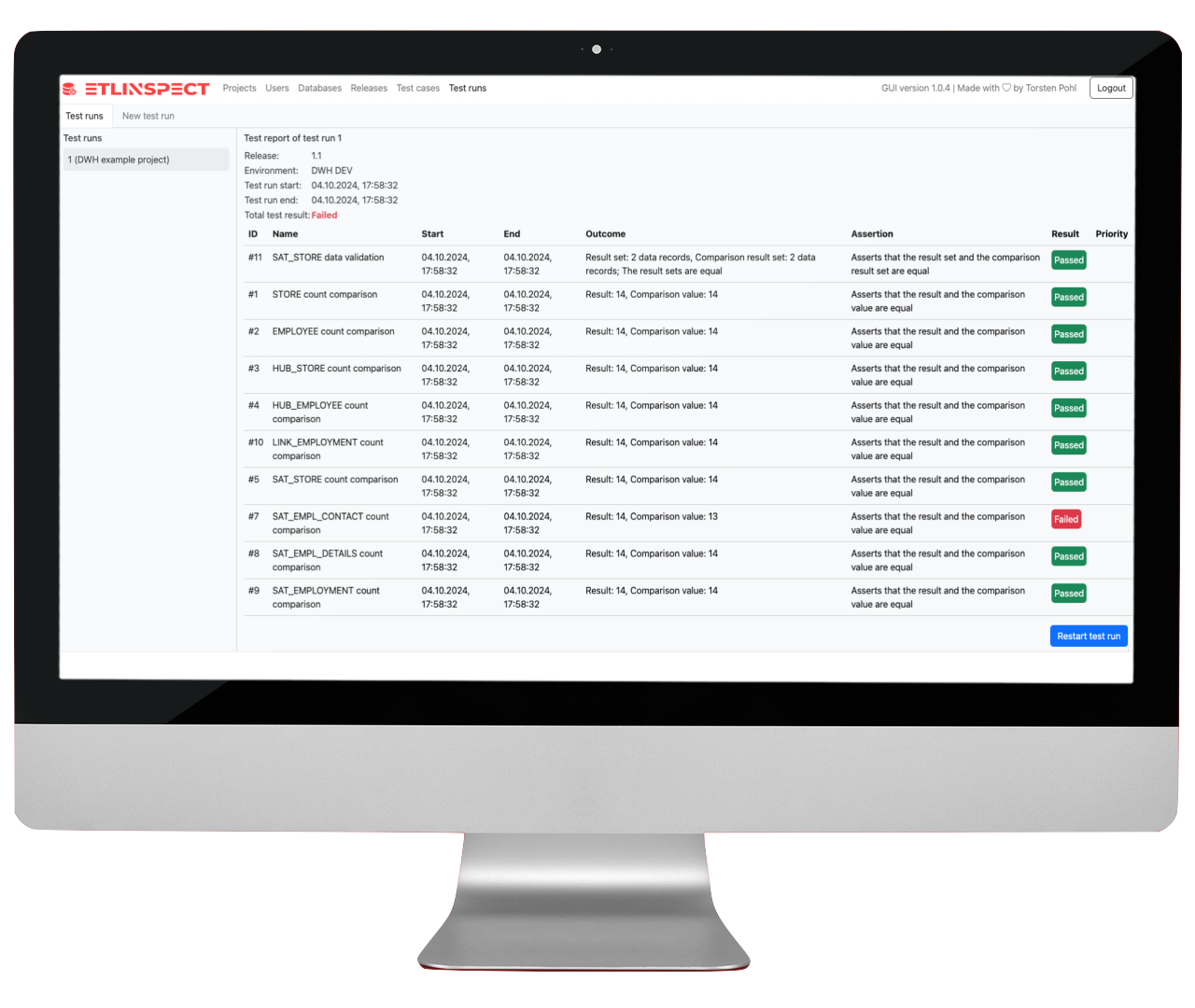
data, it is crucial to automate as much as possible, and this is why ETLinspect is based on
this ETL testing process.
Categories of tests
The test levels of the test pyramid
The test pyramid is a valuable model for illustrating the different levels of software testing. At the
bottom, unit tests check whether the components of the code function properly. In the middle, integration
tests ensure that all components work together smoothly. At the top are the necessary system tests that test
the entire system's functionality, performance, security, and reliability. Most tests should occur at the
base of the pyramid, as unit tests can be performed quickly and efficiently and cover a wide range of error
sources.
Functional vs. non-functional
Functional tests focus on verifying the functionality of systems and applications. They check whether the
various functions and components meet their requirements – correctly and completely. Non-functional
tests, on the other hand, relate to performance, scalability, security, user-friendliness, and
compatibility. Here, it is tested how the system reacts in different situations, how fast it works, and how
easy it is to use. The security of confidential data is also tested here.
The sense and nonsense of test categorization
Testing is a complex task as many aspects need to be considered. One way to structure and make the process
more efficient is to categorize tests. These categories help prioritize and ensure that all necessary tests
are performed.
However, there is no clear boundary between categories, and assigning tests clearly can be challenging. It
is, therefore, essential to remain flexible and choose an individual testing strategy that ensures all
relevant tests are performed. Nevertheless, categories can serve as a rough orientation to ensure that the
tested system or application meets the requirements, no matter what they are.
Sequential vs. iterative software development
models
The world of software development offers various models for handling projects in structured ways. One of
these models is the sequential, also known as the waterfall model. In this model, fixed phases are completed
one after the other before moving on to the next. It is a good choice for projects with precise and stable
requirements. However, iterative models, such as Scrum, divide the development process into recurring cycles
and can thus respond more flexibly to changes or still-unknown circumstances. This is an approach for
projects where requirements may change or are not yet fully known.
Sequential or iterative? Both have their advantages and disadvantages. However, regardless of the chosen
model, test cases should be created so that they can be used for all phases of development and can also be
used for regression testing, because test cases are not just a small part of the development process but an
integral part that should be created from the beginning and updated continuously.
What are the minimum requirements for ETL testing?
Effective ETL testing ensures that data is correctly extracted, transformed, and loaded. But what is the
minimum level of testing that should be performed?
Fundamentally, the following aspects should be verified:
- Verification of data volume: Does the amount of data transferred during an ETL load run
match expectations? Filters, data additions and updates, as well as historization, should be tested.
ETLinspect provides several assertions to do this.
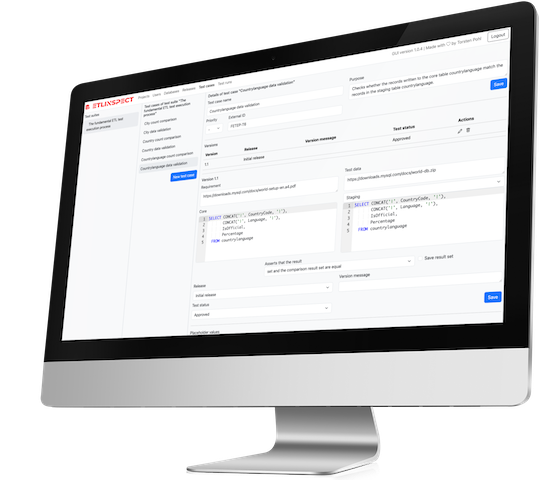
- Validation of data content: Do the transformed and loaded data match the expected
results in terms of content? In particular, mapping rules should be checked. Besides the assertions
already mentioned, ETLinspect provides the ability to define various expected result
sets for the validation of data.
- Functional Tests: Depending on the technical implementation, additional functional checks are required,
including:
- Correct updating and historization of data
- Restartability of ETL jobs after a failure
Additionally, in many systems, referential integrity in the database is disabled for performance reasons. In
such cases, ensuring referential integrity through ETL testing is essential.
Ultimately, ETL tests are as individual as the respective requirements – careful planning and
adaptation to the specific conditions of a project are therefore indispensable.
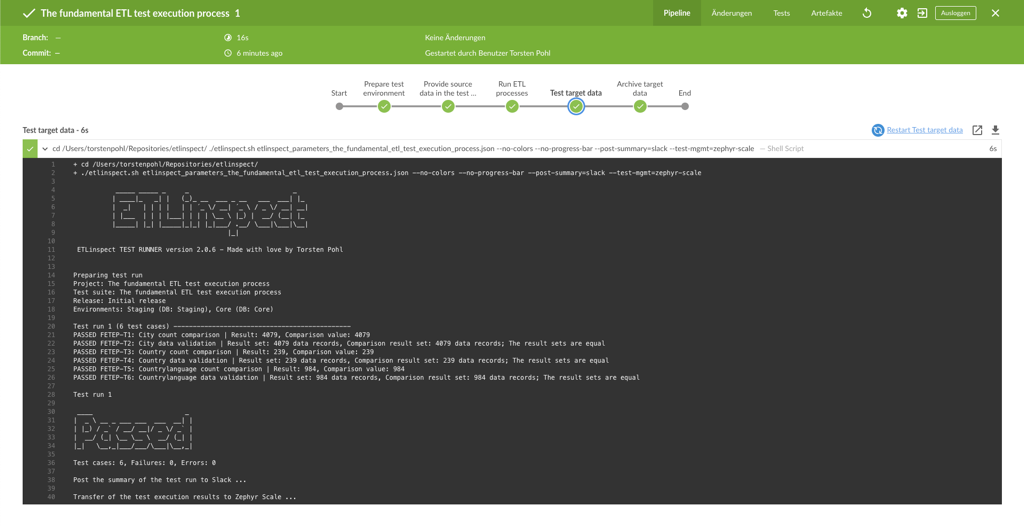
The fundamental ETL test execution process
- Prepare the test environment
- Provide source data in the test environment
- Run ETL processes
- Test target data
- Archive target data
In particular, to execute historization tests, performing all or parts of the steps in several iterations
with different data sets may be necessary.
In combination with a continuous integration tool (e.g. Jenkins),
ETLinspect is easily suitable for executing and reporting these steps, no matter how your
environments are structured.
Based on this test execution platform, the challenge for ETL testers is to design the test data and test
cases in such a way that they check all the necessary functional and non-functional aspects.
Standards and norms in ETL testing
As an ETL tester, it's essential to understand the standards and norms that guide the software testing field.
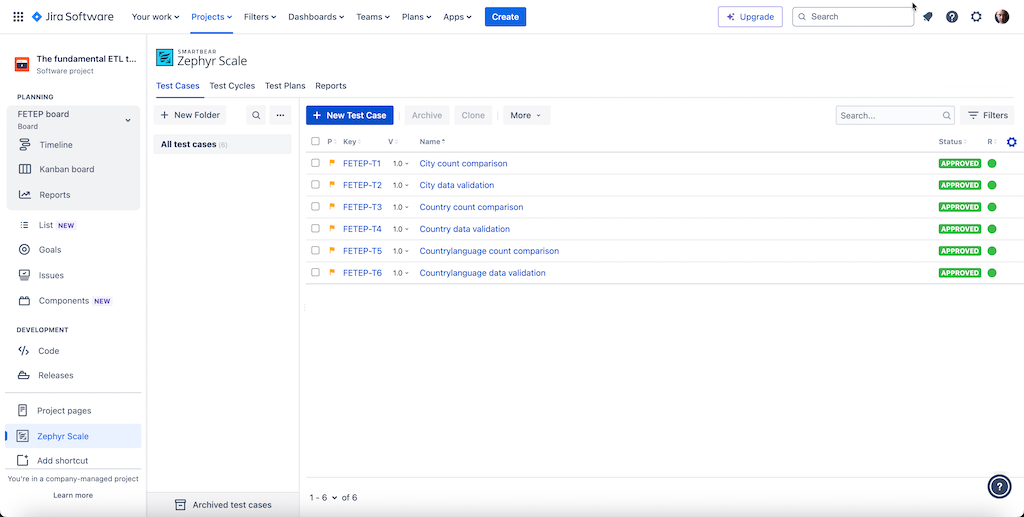
ETLinspect provides the basis for this in its capabilities for documenting test cases,
organizing test suites, and test reporting. This knowledge helps to ensure test accuracy, reproducibility,
and overall effectiveness. Here are some of the key standards and norms that you should know.
- IEEE 829-2008 Standard for Software and System Test Documentation: Developed by the Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the IEEE 829 standard outlines the format of software test
documentation.
- ISO/IEC/IEEE 29119 Software Testing: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) published
the ISO 29119 standard. This set of international standards for software testing includes test
processes, test documentation, test case design techniques, and test management.
- IEEE 730-2014 Standard for Software Quality Assurance Processes: This standard outlines creating a
software quality assurance plan.
- ISTQB: The International Software
Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB) doesn't set specific standards but offers a widely recognized
certification program. Their syllabus and materials can provide valuable guidelines for understanding
software testing, including ETL testing.
- Agile and DevOps Principles: Though not formal standards or norms, Agile and DevOps principles have
become industry norms in managing software testing. Agile's iterative development process encourages
continuous integration and testing, making it crucial for ETL testers. DevOps, on the other hand,
emphasizes the collaboration between development and operations teams, reinforcing the role of
continuous testing throughout the software development lifecycle. Find more on Agile principles at www.agilealliance.org.
Find information on DevOps at aws.amazon.com.
Remember, standards and norms should guide your ETL testing process. They exist to ensure quality and
consistency in testing practices. However, you may need to adapt these standards to the specific needs of
your project or organization.